A drug-resistant and possibly lethal fungus has been spreading quickly as a result of U.S. overall health treatment facilities, a new federal government study finds.
The fungus, a form of yeast identified as Candida auris, or C. auris, can lead to significant illness in individuals with weakened immune methods. The selection of people today identified with bacterial infections — as perfectly as the number of these who had been observed through screening to be carrying C. auris — has been growing at an alarming amount since it was first reported in the U.S., researchers from the Facilities for Ailment Regulate and Prevention documented Monday.
The improves, “especially in the most modern many years, are truly concerning to us,” the study’s lead writer, Dr. Meghan Lyman, main health care officer in the CDC’s Mycotic Health conditions Department, claimed in an job interview. “We’ve witnessed increases not just in parts of ongoing transmission, but also in new areas.”
The CDC’s new warning, posted in the Annals of Interior Medicine, comes as the Mississippi Division of Health and fitness is battling a expanding outbreak of the fungus. Given that November, at the very least 12 individuals have been contaminated with C. auris with four “likely affiliated fatalities,” the state’s epidemiologist Dr. Paul Byers, said in an e-mail.
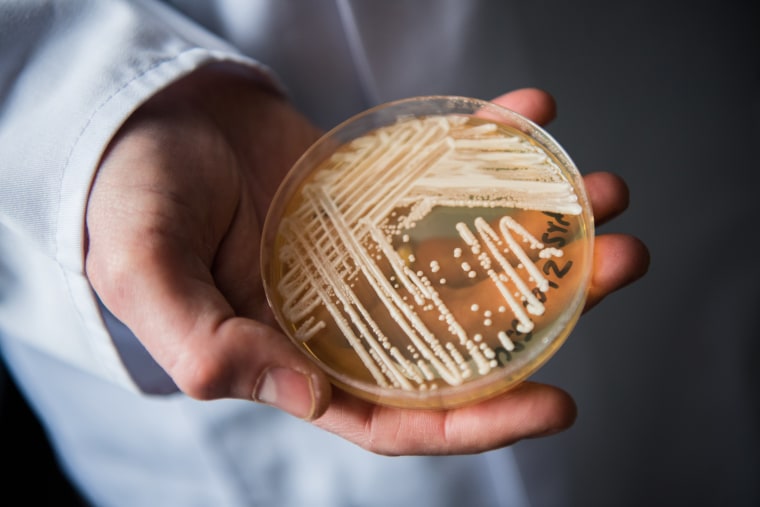

There has been ongoing transmission at two long-term treatment amenities, though instances have been identified at quite a few other amenities in the state.
“Regretably, multi-drug resistant organisms this kind of as C. auris have become far more widespread among the our highest danger persons, such as inhabitants in extended-term care facilities,” Byers claimed.
The fungus can be observed on the pores and skin and throughout the system, according to the CDC. It really is not a danger to healthier people today, but about one particular-3rd of people who develop into unwell with C. auris die.
In the CDC report, researchers analyzed state and neighborhood wellbeing department data on persons sickened by the fungus from 2016 by way of Dec. 31, 2021, as very well as those people who were “colonized,” which means they were being not sick but were carrying it on their bodies with the possible of transmitting it to some others who may well be extra susceptible to it.
The selection of bacterial infections improved by 59{7b6cc35713332e03d34197859d8d439e4802eb556451407ffda280a51e3c41ac}, to 756, from 2019 to 2020 and then by an more 95{7b6cc35713332e03d34197859d8d439e4802eb556451407ffda280a51e3c41ac}, to 1,471, in 2021.
The researchers also discovered that the incidence of people not contaminated with the fungus but colonized by it increased by 21{7b6cc35713332e03d34197859d8d439e4802eb556451407ffda280a51e3c41ac} in 2020, as opposed to 2019, and by 209{7b6cc35713332e03d34197859d8d439e4802eb556451407ffda280a51e3c41ac} in 2021, with an maximize to 4,041 in 2021 compared to 1,310 in 2020.
C. auris has now been detected in extra than fifty percent of U.S. states, the new research observed.