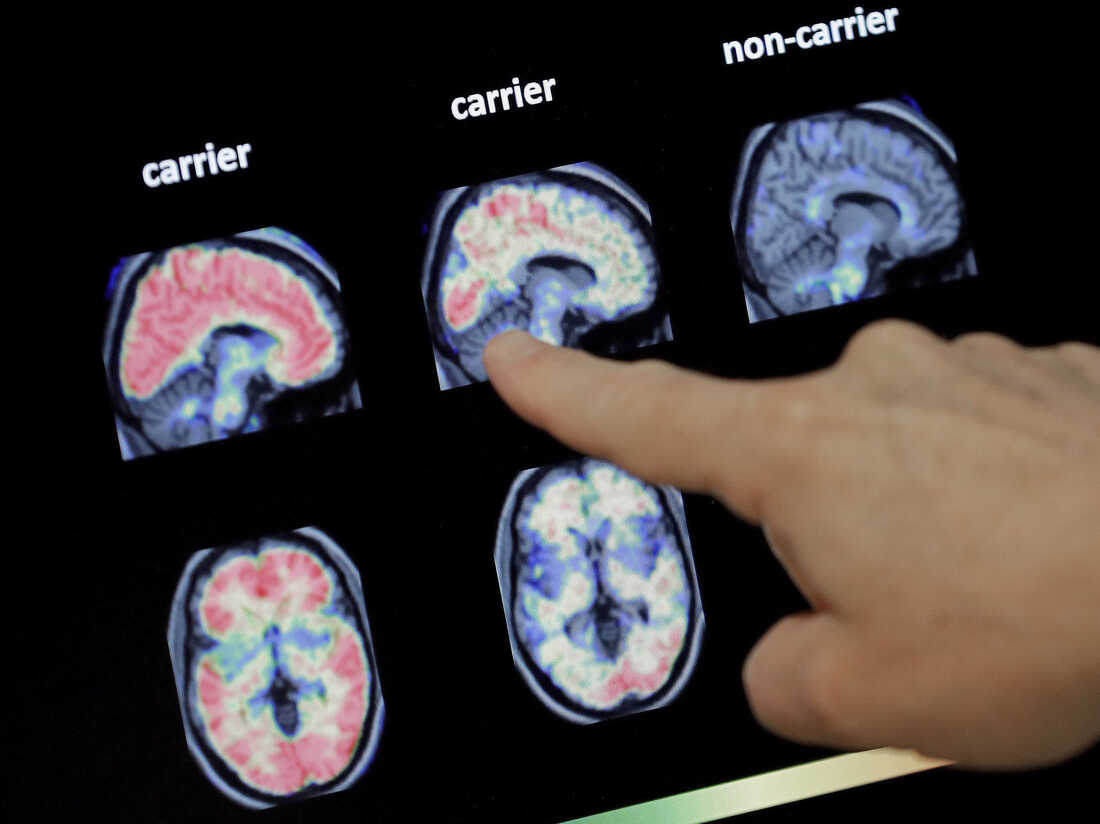
Scientists say research into Alzheimer’s wants to choose a broader see of how the ailment affects the brain — whether or not that is variations in the cortex or the role of irritation.
Matt York/AP
disguise caption
toggle caption
Matt York/AP
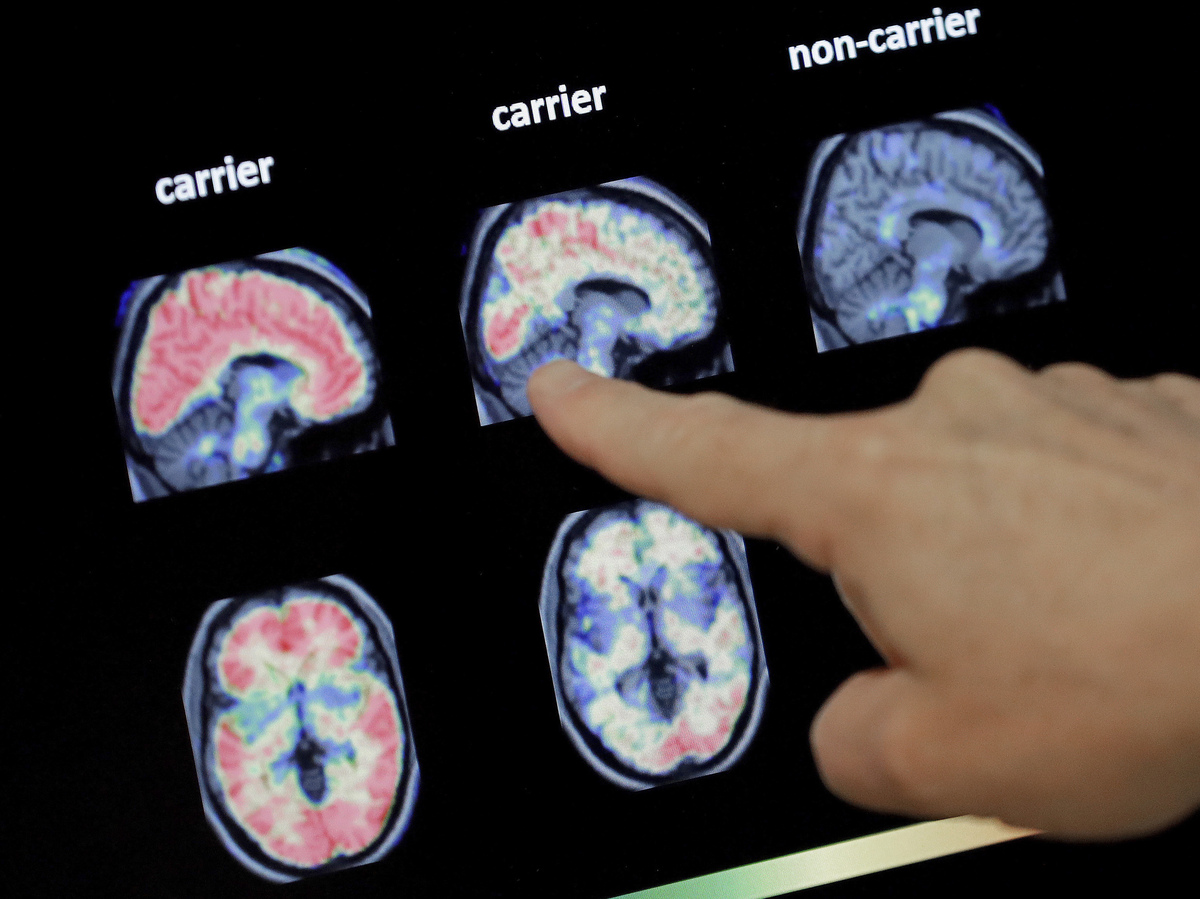
Scientists say investigation into Alzheimer’s needs to choose a broader look at of how the sickness influences the brain — whether which is modifications in the cortex or the position of inflammation.
Matt York/AP
The industry of Alzheimer’s investigate is branching out.
Immediately after a long time of concentrating on the sticky amyloid plaques and tangled tau fibers affiliated with the illness, brain scientists are seeking for other likely triggers of impaired memory and contemplating.
That search is on full display this 7 days at the Alzheimer’s Affiliation Global Meeting in San Diego, in which periods are discovering variables which includes genes, mind personal injury, clogged arteries and irritation.
A group of researchers from Seattle even unveiled a remarkably detailed atlas demonstrating how distinct forms of mind cells adjust in Alzheimer’s. The purpose is to enable researchers establish new methods to procedure.
“Absolutely, plaques and tangles are a hallmark,” says Maria Carrillo, chief science officer of the Alzheimer’s Affiliation. “It will not suggest plaques are the cause of mobile demise.”
Plaques are clumps of a protein termed beta-amyloid that appear in the areas amongst neurons. Tangles are designed up of a protein termed tau that appears inside of a neuron.
Both proteins have a tendency to accumulate in the brains of persons with Alzheimer’s. But their job in killing mind cells is even now unclear.
Carrillo suggests the Alzheimer’s discipline requirements to glimpse to cancer exploration exactly where a deeper knowing of the ailment has led to better treatments.
The shift comes after a collection of experimental prescription drugs have succeeded in eliminating amyloid plaques and tau tangles from the mind, but failed to halt the ailment.
The Foodstuff and Drug Administration has approved one particular amyloid drug, Aduhelm, but is continue to evaluating regardless of whether it in fact aids people.
An Alzheimer’s Atlas
The study that created the atlas is emblematic of how scientists are recalibrating.
“What we are hoping to do with this study is to seem at mobile vulnerability early on in sickness, just before [people] have plaques and tangles, prior to they have cognitive impairment,” states Dr. C. Dirk Keene, a neuropathologist at the University of Washington.
To develop the atlas, Keene and a staff of researches analyzed a lot more than a million cells from 84 brains donated by people who’d signed up for Alzheimer’s exploration jobs operate by the University of Washington and Kaiser Permanente Washington Research Institute.
The brains arrived from donors “at all different stages of illness” Keene says, “so we can pinpoint what is taking place from the earliest levels all the way through to men and women with sophisticated disorder.”
The hard work is funded by the National Institute on Growing old and grew out of the federal Brain initiative launched by President Obama in 2013.
The atlas arrived from the realization that “If we want to handle conditions of an extremely intricate cellular organ, you will need to have an understanding of that organ substantially much better than we do,” suggests Ed Lein, a senior investigator at the Allen Institute for Brain Science, which performed a crucial part in analyzing the brain tissue.
So the group used years studying cells in wholesome brains in advance of wanting at brains impacted by Alzheimer’s.
“We have described what a typical adult brain appears like,” Lein claims, “and now we can use that expertise and look for changes that are happening in specific sorts of cells.”

Locating susceptible brain cells
At the Alzheimer’s meeting, the team described adjustments they noticed in a lot more than 100 forms of cells taken from the cortex — an place of the mind which is significant to memory and contemplating.
One particular discovering was that neurons that make connections within just the cortex itself have been considerably much more most likely to die than people that connect to distant parts of the mind.
“What we’re viewing is a profound influence on cortical circuitry that quite plausibly is the rationale we have cognitive drop,” Lein states.
If so, a procedure designed to guard those people vulnerable neurons may avert declines in memory and pondering linked to Alzheimer’s.
The group also identified a proliferation of brain cells that lead to swelling. These involved particular immune cells and a sort of cell that responds to damage.
“So even though the neurons are lost, the non-neuronal cells are basically raising and modifying” Lein claims.
The discovering supports the idea that irritation plays an critical position in Alzheimer’s, and that anti-inflammatory medicine may well enable shield the brain.
The Seattle group hopes other scientists will use the mind mobile atlas to appear up with new treatment plans for Alzheimer’s.
“We’ve produced an open-obtain resource where the full local community can appear and glance at this information,” Lein says. “They can mine it to pace up progress in the subject as a full.”
Dashing up development is a single reason Kyle Travaglini, a researcher at the Allen Institute, jumped at the chance to do the job on the Alzheimer’s task.
“My grandmother commenced producing Alzheimer’s sickness when I was just going off to higher education,” suggests Travaglini, who gained his PhD in 2021.
Travaglini suggests the atlas task is captivating for the reason that it isn’t based on a preconceived strategy about what brings about Alzheimer’s.
“It really is like looking at the identical sickness that all people has been wanting at but in an solely distinct way,” he claims.



